
Nash equilibrium can be observed in many business settings, particularly in situations where multiple firms are competing with each other.
Nash equilibrium is a game theory concept that defines a situation in which each player in a game has selected the optimum strategy in response to the tactics adopted by the other players. In other words, given the strategies of the other players, no player has the incentive to modify their strategy unilaterally in a Nash equilibrium.
Consider a market in which two firms, A and B, are competing to sell a particular product. Each firm has two pricing strategies available: a high price or a low price. The profits that each firm can earn from the different pricing strategies are shown in the following table:
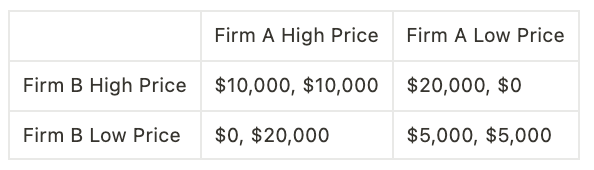
In this game, the dominant strategy for both firms is to set a low price, regardless of what the other firm does. This is because setting a high price will result in lower profits for the firm, regardless of what the other firm does.
However, if both firms choose to set a low price, they will end up in a Nash equilibrium, where neither firm can increase its profits by unilaterally changing its strategy. This is because if either firm raises its price, it will lose market share to the other firm and end up with lower profits than if it had maintained a low price.
Therefore, in this example, the Nash equilibrium is for both firms to set a low price. This equilibrium represents a stable outcome, where neither firm has the incentive to change its strategy.
Nash equilibrium may also be used to finance, notably in the context of financial corporations’ strategic decision-making. Here are a couple of such examples:
- Oligopoly Pricing: Nash equilibrium can be used to represent the pricing strategies of oligopolistic enterprises, such as those in the banking industry. A limited number of businesses dominate the market under an oligopoly, and each firm’s pricing approach has a considerable influence on the market. Firms can use game theory to forecast the optimum pricing approach to maximize profits while taking their competitors’ behaviors into account.
- Stock Market Trading: Nash equilibrium may be used to forecast the behavior of stock market traders. For example, if two traders each have a strategy to purchase a certain stock when its price is low, they may both end up buying the stock at the same time, causing the price to rise. The Nash equilibrium in this example would be for both traders to continue purchasing the stock until the price reached a particular level, at which point they would sell the stock to maximize their gains.
- Investment Decisions: Nash equilibrium can be used to forecast competing enterprises’ investment choices. For example, if two businesses are debating whether to participate in a specific project, each may have a strategy to invest only if the other firm also invests. In this situation, the Nash equilibrium would be for both businesses to invest, because neither firm can increase its payout by altering its strategy unilaterally.
Nash equilibrium provides a valuable framework for analysing financial organisations’ strategic decision-making and anticipating their behaviour in competitive scenarios.